 Niels Bohr (1885-1962), a Danish physicist, founded the modern
quantum theory of matter. He is best known for his investigations
of atomic structure and radiation, for which he won the 1922 Nobel
Prize for physics.
Niels Bohr (1885-1962), a Danish physicist, founded the modern
quantum theory of matter. He is best known for his investigations
of atomic structure and radiation, for which he won the 1922 Nobel
Prize for physics.
 Max Born (1882-1970), a German theoretical physicist,
was a pioneer in developing quantum mechanics.
In collaboration with his students and assistants Werner Heisenberg,
Pascual Jordan, and Wolfgang Pauli, he attempted to develop a new
quantum mechanics. When Heisenberg succeeded in 1925, Born and
others were able to advance the theory, using more systematic and
powerful mathematics. For Born's interpretation of the square of
Schrodinger's wave function as the probability of an electron's
position, and for his further clarification of the wave-particle
duality, he was awarded the Nobel Prize for physics in 1954.
Max Born (1882-1970), a German theoretical physicist,
was a pioneer in developing quantum mechanics.
In collaboration with his students and assistants Werner Heisenberg,
Pascual Jordan, and Wolfgang Pauli, he attempted to develop a new
quantum mechanics. When Heisenberg succeeded in 1925, Born and
others were able to advance the theory, using more systematic and
powerful mathematics. For Born's interpretation of the square of
Schrodinger's wave function as the probability of an electron's
position, and for his further clarification of the wave-particle
duality, he was awarded the Nobel Prize for physics in 1954.
 Nicolaus Copernicus (1473-1543) was the Polish astronomer who
revolutionized science and the conception of the universe with his
heliocentric theory of planetary movement, published as De
revolutionibus orbium coelestium (1543).
Nicolaus Copernicus (1473-1543) was the Polish astronomer who
revolutionized science and the conception of the universe with his
heliocentric theory of planetary movement, published as De
revolutionibus orbium coelestium (1543).
 Marie Curie (1867-1934), a French physicist, shown in her laboratory
in a colored photograph taken in 1905, is best known for her work
in the study of radioactivity. Together with her husband, Pierre,
she shared the 1903 Nobel Prize for physics, and she received the
prize for chemistry in 1911.
Marie Curie (1867-1934), a French physicist, shown in her laboratory
in a colored photograph taken in 1905, is best known for her work
in the study of radioactivity. Together with her husband, Pierre,
she shared the 1903 Nobel Prize for physics, and she received the
prize for chemistry in 1911.
 Louis de Broglie (1892-1987), a French physicist,
is known for his theory that matter has the
properties of both particles and waves. This particle-wave
duality, derived from the work of Albert Einstein and Max Planck,
was experimentally confirmed, for the electron, in 1927. De
Broglie received the 1929 Nobel Prize for physics.
Louis de Broglie (1892-1987), a French physicist,
is known for his theory that matter has the
properties of both particles and waves. This particle-wave
duality, derived from the work of Albert Einstein and Max Planck,
was experimentally confirmed, for the electron, in 1927. De
Broglie received the 1929 Nobel Prize for physics.
 Paul Dirac (1902-1984) was awarded the 1933 Nobel Prize for physics for
his modification of Schrodinger's wave equation, the mathematical
theory describing the motion of atomic particles. Dirac, who shared
the award with Schrodinger, applied relativity theory to quantum
mechanics in predicting the existence of positrons and electron
spin.
Paul Dirac (1902-1984) was awarded the 1933 Nobel Prize for physics for
his modification of Schrodinger's wave equation, the mathematical
theory describing the motion of atomic particles. Dirac, who shared
the award with Schrodinger, applied relativity theory to quantum
mechanics in predicting the existence of positrons and electron
spin.
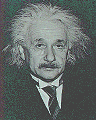 Albert Einstein (1879-1955), a German-American physicist,
revolutionized the assumptions of modern physics when he first
published his theory of relativity in 1905.
Albert Einstein (1879-1955), a German-American physicist,
revolutionized the assumptions of modern physics when he first
published his theory of relativity in 1905.
 Michael Faraday (1791-1867), an English chemist and physicist, is
shown here in an early daguerreotype holding a bar of glass he used
in his 1845 experiments on the effects of a magnetic field on
polarized light. Faraday is considered by many scientists to be
the greatest experimentalist ever.
Michael Faraday (1791-1867), an English chemist and physicist, is
shown here in an early daguerreotype holding a bar of glass he used
in his 1845 experiments on the effects of a magnetic field on
polarized light. Faraday is considered by many scientists to be
the greatest experimentalist ever.
 Enrico Fermi (1901-1954) conducted the experiments in radioactivity
that won him the 1938 Nobel Prize for physics before emigrating
from Italy to the United States and commencing work on the atomic
bomb. An exceptional researcher and theorist, Fermi developed a
statistical method for predicting the behavior of atomic particles
and later led the group that achieved the first self-sustaining
fission reaction.
Enrico Fermi (1901-1954) conducted the experiments in radioactivity
that won him the 1938 Nobel Prize for physics before emigrating
from Italy to the United States and commencing work on the atomic
bomb. An exceptional researcher and theorist, Fermi developed a
statistical method for predicting the behavior of atomic particles
and later led the group that achieved the first self-sustaining
fission reaction.
 Richard Phillips Feynman (1918-1988), an American physicist
contributed to the joining of relativity
and quantum theory with electromagnetism to form quantum
electrodynamics. He is also known for his reformulation of
quantum mechanics and his research on liquid helium. In 1965 he
shared the Nobel Prize for physics with Julian Schwinger and Sin
Itiro Tomonago for their contributions to electrodynamics.
Richard Phillips Feynman (1918-1988), an American physicist
contributed to the joining of relativity
and quantum theory with electromagnetism to form quantum
electrodynamics. He is also known for his reformulation of
quantum mechanics and his research on liquid helium. In 1965 he
shared the Nobel Prize for physics with Julian Schwinger and Sin
Itiro Tomonago for their contributions to electrodynamics.
 Edmond Halley (1656-1742), an English astronomer and mathematician,
is depicted in a 17th century colored engraving. Halley was the
first to calculate the orbit of the comet that is named for him.
Edmond Halley (1656-1742), an English astronomer and mathematician,
is depicted in a 17th century colored engraving. Halley was the
first to calculate the orbit of the comet that is named for him.
 Stephen Hawking (1942- ), who has been paralyzed by Lou Gehrig's
disease, is confined to a wheelchair and requires a voice
synthesizer to speak. One of the world's top mathematical
physicists, he has sought to link quantum mechanics and relativity,
the two major theories of modern physics.
Stephen Hawking (1942- ), who has been paralyzed by Lou Gehrig's
disease, is confined to a wheelchair and requires a voice
synthesizer to speak. One of the world's top mathematical
physicists, he has sought to link quantum mechanics and relativity,
the two major theories of modern physics.
 Werner Karl Heisenberg (1901-1976), a German theoretical physicist
was one of the leading scientists of the
20th century. He did important work in nuclear and particle
physics, but his most significant contribution was to the
development of quantum mechanics. He is best known for his
uncertainty principle, which restricts the accuracy with which
some properties of atoms and particles--such as position and
In 1932 he was awarded the Nobel Prize in physics.
Werner Karl Heisenberg (1901-1976), a German theoretical physicist
was one of the leading scientists of the
20th century. He did important work in nuclear and particle
physics, but his most significant contribution was to the
development of quantum mechanics. He is best known for his
uncertainty principle, which restricts the accuracy with which
some properties of atoms and particles--such as position and
In 1932 he was awarded the Nobel Prize in physics.
 Edwin Powell Hubble (1889-1953), an American astronomer and the
founder of extragalactic astronomy, was a Rhodes scholar at Oxford
and began his career as a lawyer. After a year of practicing law,
he returned to graduate school and earned a doctorate in astronomy.
His accomplishments include the discovery of galaxies beyond the
Milky Way Galaxy and of the velocity-distance relationship of
galaxies.
Edwin Powell Hubble (1889-1953), an American astronomer and the
founder of extragalactic astronomy, was a Rhodes scholar at Oxford
and began his career as a lawyer. After a year of practicing law,
he returned to graduate school and earned a doctorate in astronomy.
His accomplishments include the discovery of galaxies beyond the
Milky Way Galaxy and of the velocity-distance relationship of
galaxies.
 Lord Kelvin (1824-1907), a Scottish physicist and mathematician
calculated that molecular motion stops at -273 deg C. He called
this temperature absolute zero, the lowest possible temperature. A
prodigy in mathematics, Kelvin gained his greatest renown in
thermodynamics.
Lord Kelvin (1824-1907), a Scottish physicist and mathematician
calculated that molecular motion stops at -273 deg C. He called
this temperature absolute zero, the lowest possible temperature. A
prodigy in mathematics, Kelvin gained his greatest renown in
thermodynamics.
 Johannes Kepler (1571-1630), a German mathematician, formulated the
three laws of planetary motion that bear his name by using the
astronomical observations of by Tycho Brahe, for whom he worked
briefly. Kepler was instrumental in the development of early
telescopes. He invented the convex eyepiece, which allowed an
expanded field of vision, and discovered a means of determining the
magnifying power of lenses.
Johannes Kepler (1571-1630), a German mathematician, formulated the
three laws of planetary motion that bear his name by using the
astronomical observations of by Tycho Brahe, for whom he worked
briefly. Kepler was instrumental in the development of early
telescopes. He invented the convex eyepiece, which allowed an
expanded field of vision, and discovered a means of determining the
magnifying power of lenses.
 Irving Langmuir (1881-1957), an American physical chemist, was
awarded the Nobel Prize for chemistry in 1932 for his work on
molecular films on solid and liquid surfaces. His studies in
high-temperature chemistry led to the improvement of the
tungsten-filament light bulb and the development of an atomic
hydrogen blowtorch.
Irving Langmuir (1881-1957), an American physical chemist, was
awarded the Nobel Prize for chemistry in 1932 for his work on
molecular films on solid and liquid surfaces. His studies in
high-temperature chemistry led to the improvement of the
tungsten-filament light bulb and the development of an atomic
hydrogen blowtorch.
 James Clerk Maxwell (1831-1879), the Scottish physicist,
did revolutionary work in electromagnetism and
the kinetic theory of gases.
He formulated,
independently of Ludwig Boltzmann, the Maxwell-Boltzmann
kinetic theory of gases.
Maxwell showed that a few
relatively simple mathematical equations could express the
behavior of electric and magnetic fields and their interrelated
nature. These four partial differential equations
first appeared in fully developed form in Electricity and
Magnetism (1873). Since known as Maxwell's equations they are one
of the great achievements of 19th-century physics.
James Clerk Maxwell (1831-1879), the Scottish physicist,
did revolutionary work in electromagnetism and
the kinetic theory of gases.
He formulated,
independently of Ludwig Boltzmann, the Maxwell-Boltzmann
kinetic theory of gases.
Maxwell showed that a few
relatively simple mathematical equations could express the
behavior of electric and magnetic fields and their interrelated
nature. These four partial differential equations
first appeared in fully developed form in Electricity and
Magnetism (1873). Since known as Maxwell's equations they are one
of the great achievements of 19th-century physics.
 Robert Andrews Millikan, b. Morrison (1868-1953), an American physicist,
determined through an
oil-drop experiment the value of the charge on an electron and
demonstrated that the charge was a discrete constant rather than
a statistical average. For this work, as well as for his work on
the photoelectric effect, he received the Nobel Prize for physics
in 1923.
Robert Andrews Millikan, b. Morrison (1868-1953), an American physicist,
determined through an
oil-drop experiment the value of the charge on an electron and
demonstrated that the charge was a discrete constant rather than
a statistical average. For this work, as well as for his work on
the photoelectric effect, he received the Nobel Prize for physics
in 1923.
 Sir Isaac Newton (1643-1727), one of the most important figures in
the history of science, made significant contributions in the
fields of physics, astronomy, and mathematics. In his Principia
(1687) -- considered by many the greatest work of modern science
--he explained the laws of motion and universal gravitation.
Sir Isaac Newton (1643-1727), one of the most important figures in
the history of science, made significant contributions in the
fields of physics, astronomy, and mathematics. In his Principia
(1687) -- considered by many the greatest work of modern science
--he explained the laws of motion and universal gravitation.
 Blaise Pascal (1623-1662), a French thinker. His
early scientific investigations
led to invaluable contributions in
mathematics and physics. He is also remembered for his
introspective religious and philosophical writings, most notably
his Pensees, which focused on the power of divine faith.
Blaise Pascal (1623-1662), a French thinker. His
early scientific investigations
led to invaluable contributions in
mathematics and physics. He is also remembered for his
introspective religious and philosophical writings, most notably
his Pensees, which focused on the power of divine faith.
 Wolfgang Ernst Pauli (1900-1958), an Austrian theoretical physicist,
was one of the founders of modern
physics. He is most famous for his "Pauli exclusion principle,"
which states that no two electrons in an atom can have the same
four quantum numbers. For his work in
this area he was awarded the 1945 Nobel Prize for physics.
Wolfgang Ernst Pauli (1900-1958), an Austrian theoretical physicist,
was one of the founders of modern
physics. He is most famous for his "Pauli exclusion principle,"
which states that no two electrons in an atom can have the same
four quantum numbers. For his work in
this area he was awarded the 1945 Nobel Prize for physics.
 Max Planck (1858-1947), a German physicist, revolutionized physics in
1900 with his discovery of the quantum, or fundamental unit of
energy. Planck received the Nobel Prize for physics in 1918 in
recognition of his breakthrough. He is shown in a photograph taken
in 1947, the year of his death.
Max Planck (1858-1947), a German physicist, revolutionized physics in
1900 with his discovery of the quantum, or fundamental unit of
energy. Planck received the Nobel Prize for physics in 1918 in
recognition of his breakthrough. He is shown in a photograph taken
in 1947, the year of his death.
 Wilhelm Conrad Roentgen (1845-1923), a German physicist, received the
first Nobel Prize for physics (1901) for his discovery of X rays.
Wilhelm Conrad Roentgen (1845-1923), a German physicist, received the
first Nobel Prize for physics (1901) for his discovery of X rays.
 Sir Ernest Rutherford (1871-1937) profoundly influenced modern
physics by formulating the first explanation of radioactivity. He
discovered two basic forms of radioactivity and in 1908 received
the Nobel Prize for chemistry for this work. He announced his
greatest discovery--the nuclear structure of the atom--in 1911.
Sir Ernest Rutherford (1871-1937) profoundly influenced modern
physics by formulating the first explanation of radioactivity. He
discovered two basic forms of radioactivity and in 1908 received
the Nobel Prize for chemistry for this work. He announced his
greatest discovery--the nuclear structure of the atom--in 1911.
 Erwin Schrodinger (1887-1961), an Austrian theoretical physicist,
published (1926) four papers that laid the
foundation of the wave-mechanics approach to quantum theory and
set forth his now-famous wave equation.
In 1933 he shared the
Nobel Prize for physics with Paul DIRAC for his contributions to
atomic theory.
He also worked on problems of general relativity and cosmology
and on a unified field theory. Late in his life Schrodinger
studied the foundations of physics and their implications for
philosophy.
Erwin Schrodinger (1887-1961), an Austrian theoretical physicist,
published (1926) four papers that laid the
foundation of the wave-mechanics approach to quantum theory and
set forth his now-famous wave equation.
In 1933 he shared the
Nobel Prize for physics with Paul DIRAC for his contributions to
atomic theory.
He also worked on problems of general relativity and cosmology
and on a unified field theory. Late in his life Schrodinger
studied the foundations of physics and their implications for
philosophy.
 Sir Joseph John Thomson (1856-1940), a pioneer in modern physics,
discovered the electron in 1895, revolutionizing existing theories
of atomic structure. Thomson is also recognized for his
investigations into the conduction of electricity through
gases--which earned him the 1906 Nobel Prize for physics--and for
his work on the mathematics of the electromagnetic-field theory
proposed by James Maxwell.
Sir Joseph John Thomson (1856-1940), a pioneer in modern physics,
discovered the electron in 1895, revolutionizing existing theories
of atomic structure. Thomson is also recognized for his
investigations into the conduction of electricity through
gases--which earned him the 1906 Nobel Prize for physics--and for
his work on the mathematics of the electromagnetic-field theory
proposed by James Maxwell.
 Hideki Yukawa (1907-1981), a Japanese physicist,
who won the Nobel Prize for physics in 1949, is known
for his theory of how the nuclear force holds the nucleus
together. As a result of this theory, he predicted (1935) the
existence of the meson, a subatomic particle, found in 1947 by
Cecil Powell.
Hideki Yukawa (1907-1981), a Japanese physicist,
who won the Nobel Prize for physics in 1949, is known
for his theory of how the nuclear force holds the nucleus
together. As a result of this theory, he predicted (1935) the
existence of the meson, a subatomic particle, found in 1947 by
Cecil Powell.
 Niels Bohr (1885-1962), a Danish physicist, founded the modern
quantum theory of matter. He is best known for his investigations
of atomic structure and radiation, for which he won the 1922 Nobel
Prize for physics.
Niels Bohr (1885-1962), a Danish physicist, founded the modern
quantum theory of matter. He is best known for his investigations
of atomic structure and radiation, for which he won the 1922 Nobel
Prize for physics.
 Max Born (1882-1970), a German theoretical physicist,
was a pioneer in developing quantum mechanics.
In collaboration with his students and assistants Werner Heisenberg,
Pascual Jordan, and Wolfgang Pauli, he attempted to develop a new
quantum mechanics. When Heisenberg succeeded in 1925, Born and
others were able to advance the theory, using more systematic and
powerful mathematics. For Born's interpretation of the square of
Schrodinger's wave function as the probability of an electron's
position, and for his further clarification of the wave-particle
duality, he was awarded the Nobel Prize for physics in 1954.
Max Born (1882-1970), a German theoretical physicist,
was a pioneer in developing quantum mechanics.
In collaboration with his students and assistants Werner Heisenberg,
Pascual Jordan, and Wolfgang Pauli, he attempted to develop a new
quantum mechanics. When Heisenberg succeeded in 1925, Born and
others were able to advance the theory, using more systematic and
powerful mathematics. For Born's interpretation of the square of
Schrodinger's wave function as the probability of an electron's
position, and for his further clarification of the wave-particle
duality, he was awarded the Nobel Prize for physics in 1954.
 Nicolaus Copernicus (1473-1543) was the Polish astronomer who
revolutionized science and the conception of the universe with his
heliocentric theory of planetary movement, published as De
revolutionibus orbium coelestium (1543).
Nicolaus Copernicus (1473-1543) was the Polish astronomer who
revolutionized science and the conception of the universe with his
heliocentric theory of planetary movement, published as De
revolutionibus orbium coelestium (1543).
 Marie Curie (1867-1934), a French physicist, shown in her laboratory
in a colored photograph taken in 1905, is best known for her work
in the study of radioactivity. Together with her husband, Pierre,
she shared the 1903 Nobel Prize for physics, and she received the
prize for chemistry in 1911.
Marie Curie (1867-1934), a French physicist, shown in her laboratory
in a colored photograph taken in 1905, is best known for her work
in the study of radioactivity. Together with her husband, Pierre,
she shared the 1903 Nobel Prize for physics, and she received the
prize for chemistry in 1911.
 Louis de Broglie (1892-1987), a French physicist,
is known for his theory that matter has the
properties of both particles and waves. This particle-wave
duality, derived from the work of Albert Einstein and Max Planck,
was experimentally confirmed, for the electron, in 1927. De
Broglie received the 1929 Nobel Prize for physics.
Louis de Broglie (1892-1987), a French physicist,
is known for his theory that matter has the
properties of both particles and waves. This particle-wave
duality, derived from the work of Albert Einstein and Max Planck,
was experimentally confirmed, for the electron, in 1927. De
Broglie received the 1929 Nobel Prize for physics.
 Paul Dirac (1902-1984) was awarded the 1933 Nobel Prize for physics for
his modification of Schrodinger's wave equation, the mathematical
theory describing the motion of atomic particles. Dirac, who shared
the award with Schrodinger, applied relativity theory to quantum
mechanics in predicting the existence of positrons and electron
spin.
Paul Dirac (1902-1984) was awarded the 1933 Nobel Prize for physics for
his modification of Schrodinger's wave equation, the mathematical
theory describing the motion of atomic particles. Dirac, who shared
the award with Schrodinger, applied relativity theory to quantum
mechanics in predicting the existence of positrons and electron
spin.
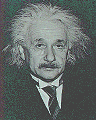 Albert Einstein (1879-1955), a German-American physicist,
revolutionized the assumptions of modern physics when he first
published his theory of relativity in 1905.
Albert Einstein (1879-1955), a German-American physicist,
revolutionized the assumptions of modern physics when he first
published his theory of relativity in 1905.
 Michael Faraday (1791-1867), an English chemist and physicist, is
shown here in an early daguerreotype holding a bar of glass he used
in his 1845 experiments on the effects of a magnetic field on
polarized light. Faraday is considered by many scientists to be
the greatest experimentalist ever.
Michael Faraday (1791-1867), an English chemist and physicist, is
shown here in an early daguerreotype holding a bar of glass he used
in his 1845 experiments on the effects of a magnetic field on
polarized light. Faraday is considered by many scientists to be
the greatest experimentalist ever.
 Enrico Fermi (1901-1954) conducted the experiments in radioactivity
that won him the 1938 Nobel Prize for physics before emigrating
from Italy to the United States and commencing work on the atomic
bomb. An exceptional researcher and theorist, Fermi developed a
statistical method for predicting the behavior of atomic particles
and later led the group that achieved the first self-sustaining
fission reaction.
Enrico Fermi (1901-1954) conducted the experiments in radioactivity
that won him the 1938 Nobel Prize for physics before emigrating
from Italy to the United States and commencing work on the atomic
bomb. An exceptional researcher and theorist, Fermi developed a
statistical method for predicting the behavior of atomic particles
and later led the group that achieved the first self-sustaining
fission reaction.
 Richard Phillips Feynman (1918-1988), an American physicist
contributed to the joining of relativity
and quantum theory with electromagnetism to form quantum
electrodynamics. He is also known for his reformulation of
quantum mechanics and his research on liquid helium. In 1965 he
shared the Nobel Prize for physics with Julian Schwinger and Sin
Itiro Tomonago for their contributions to electrodynamics.
Richard Phillips Feynman (1918-1988), an American physicist
contributed to the joining of relativity
and quantum theory with electromagnetism to form quantum
electrodynamics. He is also known for his reformulation of
quantum mechanics and his research on liquid helium. In 1965 he
shared the Nobel Prize for physics with Julian Schwinger and Sin
Itiro Tomonago for their contributions to electrodynamics.
 Edmond Halley (1656-1742), an English astronomer and mathematician,
is depicted in a 17th century colored engraving. Halley was the
first to calculate the orbit of the comet that is named for him.
Edmond Halley (1656-1742), an English astronomer and mathematician,
is depicted in a 17th century colored engraving. Halley was the
first to calculate the orbit of the comet that is named for him.
 Stephen Hawking (1942- ), who has been paralyzed by Lou Gehrig's
disease, is confined to a wheelchair and requires a voice
synthesizer to speak. One of the world's top mathematical
physicists, he has sought to link quantum mechanics and relativity,
the two major theories of modern physics.
Stephen Hawking (1942- ), who has been paralyzed by Lou Gehrig's
disease, is confined to a wheelchair and requires a voice
synthesizer to speak. One of the world's top mathematical
physicists, he has sought to link quantum mechanics and relativity,
the two major theories of modern physics.
 Werner Karl Heisenberg (1901-1976), a German theoretical physicist
was one of the leading scientists of the
20th century. He did important work in nuclear and particle
physics, but his most significant contribution was to the
development of quantum mechanics. He is best known for his
uncertainty principle, which restricts the accuracy with which
some properties of atoms and particles--such as position and
In 1932 he was awarded the Nobel Prize in physics.
Werner Karl Heisenberg (1901-1976), a German theoretical physicist
was one of the leading scientists of the
20th century. He did important work in nuclear and particle
physics, but his most significant contribution was to the
development of quantum mechanics. He is best known for his
uncertainty principle, which restricts the accuracy with which
some properties of atoms and particles--such as position and
In 1932 he was awarded the Nobel Prize in physics.
 Edwin Powell Hubble (1889-1953), an American astronomer and the
founder of extragalactic astronomy, was a Rhodes scholar at Oxford
and began his career as a lawyer. After a year of practicing law,
he returned to graduate school and earned a doctorate in astronomy.
His accomplishments include the discovery of galaxies beyond the
Milky Way Galaxy and of the velocity-distance relationship of
galaxies.
Edwin Powell Hubble (1889-1953), an American astronomer and the
founder of extragalactic astronomy, was a Rhodes scholar at Oxford
and began his career as a lawyer. After a year of practicing law,
he returned to graduate school and earned a doctorate in astronomy.
His accomplishments include the discovery of galaxies beyond the
Milky Way Galaxy and of the velocity-distance relationship of
galaxies.
 Lord Kelvin (1824-1907), a Scottish physicist and mathematician
calculated that molecular motion stops at -273 deg C. He called
this temperature absolute zero, the lowest possible temperature. A
prodigy in mathematics, Kelvin gained his greatest renown in
thermodynamics.
Lord Kelvin (1824-1907), a Scottish physicist and mathematician
calculated that molecular motion stops at -273 deg C. He called
this temperature absolute zero, the lowest possible temperature. A
prodigy in mathematics, Kelvin gained his greatest renown in
thermodynamics.
 Johannes Kepler (1571-1630), a German mathematician, formulated the
three laws of planetary motion that bear his name by using the
astronomical observations of by Tycho Brahe, for whom he worked
briefly. Kepler was instrumental in the development of early
telescopes. He invented the convex eyepiece, which allowed an
expanded field of vision, and discovered a means of determining the
magnifying power of lenses.
Johannes Kepler (1571-1630), a German mathematician, formulated the
three laws of planetary motion that bear his name by using the
astronomical observations of by Tycho Brahe, for whom he worked
briefly. Kepler was instrumental in the development of early
telescopes. He invented the convex eyepiece, which allowed an
expanded field of vision, and discovered a means of determining the
magnifying power of lenses.
 Irving Langmuir (1881-1957), an American physical chemist, was
awarded the Nobel Prize for chemistry in 1932 for his work on
molecular films on solid and liquid surfaces. His studies in
high-temperature chemistry led to the improvement of the
tungsten-filament light bulb and the development of an atomic
hydrogen blowtorch.
Irving Langmuir (1881-1957), an American physical chemist, was
awarded the Nobel Prize for chemistry in 1932 for his work on
molecular films on solid and liquid surfaces. His studies in
high-temperature chemistry led to the improvement of the
tungsten-filament light bulb and the development of an atomic
hydrogen blowtorch.
 James Clerk Maxwell (1831-1879), the Scottish physicist,
did revolutionary work in electromagnetism and
the kinetic theory of gases.
He formulated,
independently of Ludwig Boltzmann, the Maxwell-Boltzmann
kinetic theory of gases.
Maxwell showed that a few
relatively simple mathematical equations could express the
behavior of electric and magnetic fields and their interrelated
nature. These four partial differential equations
first appeared in fully developed form in Electricity and
Magnetism (1873). Since known as Maxwell's equations they are one
of the great achievements of 19th-century physics.
James Clerk Maxwell (1831-1879), the Scottish physicist,
did revolutionary work in electromagnetism and
the kinetic theory of gases.
He formulated,
independently of Ludwig Boltzmann, the Maxwell-Boltzmann
kinetic theory of gases.
Maxwell showed that a few
relatively simple mathematical equations could express the
behavior of electric and magnetic fields and their interrelated
nature. These four partial differential equations
first appeared in fully developed form in Electricity and
Magnetism (1873). Since known as Maxwell's equations they are one
of the great achievements of 19th-century physics.
 Robert Andrews Millikan, b. Morrison (1868-1953), an American physicist,
determined through an
oil-drop experiment the value of the charge on an electron and
demonstrated that the charge was a discrete constant rather than
a statistical average. For this work, as well as for his work on
the photoelectric effect, he received the Nobel Prize for physics
in 1923.
Robert Andrews Millikan, b. Morrison (1868-1953), an American physicist,
determined through an
oil-drop experiment the value of the charge on an electron and
demonstrated that the charge was a discrete constant rather than
a statistical average. For this work, as well as for his work on
the photoelectric effect, he received the Nobel Prize for physics
in 1923.
 Sir Isaac Newton (1643-1727), one of the most important figures in
the history of science, made significant contributions in the
fields of physics, astronomy, and mathematics. In his Principia
(1687) -- considered by many the greatest work of modern science
--he explained the laws of motion and universal gravitation.
Sir Isaac Newton (1643-1727), one of the most important figures in
the history of science, made significant contributions in the
fields of physics, astronomy, and mathematics. In his Principia
(1687) -- considered by many the greatest work of modern science
--he explained the laws of motion and universal gravitation.
 Blaise Pascal (1623-1662), a French thinker. His
early scientific investigations
led to invaluable contributions in
mathematics and physics. He is also remembered for his
introspective religious and philosophical writings, most notably
his Pensees, which focused on the power of divine faith.
Blaise Pascal (1623-1662), a French thinker. His
early scientific investigations
led to invaluable contributions in
mathematics and physics. He is also remembered for his
introspective religious and philosophical writings, most notably
his Pensees, which focused on the power of divine faith.
 Wolfgang Ernst Pauli (1900-1958), an Austrian theoretical physicist,
was one of the founders of modern
physics. He is most famous for his "Pauli exclusion principle,"
which states that no two electrons in an atom can have the same
four quantum numbers. For his work in
this area he was awarded the 1945 Nobel Prize for physics.
Wolfgang Ernst Pauli (1900-1958), an Austrian theoretical physicist,
was one of the founders of modern
physics. He is most famous for his "Pauli exclusion principle,"
which states that no two electrons in an atom can have the same
four quantum numbers. For his work in
this area he was awarded the 1945 Nobel Prize for physics.
 Max Planck (1858-1947), a German physicist, revolutionized physics in
1900 with his discovery of the quantum, or fundamental unit of
energy. Planck received the Nobel Prize for physics in 1918 in
recognition of his breakthrough. He is shown in a photograph taken
in 1947, the year of his death.
Max Planck (1858-1947), a German physicist, revolutionized physics in
1900 with his discovery of the quantum, or fundamental unit of
energy. Planck received the Nobel Prize for physics in 1918 in
recognition of his breakthrough. He is shown in a photograph taken
in 1947, the year of his death.
 Wilhelm Conrad Roentgen (1845-1923), a German physicist, received the
first Nobel Prize for physics (1901) for his discovery of X rays.
Wilhelm Conrad Roentgen (1845-1923), a German physicist, received the
first Nobel Prize for physics (1901) for his discovery of X rays.
 Sir Ernest Rutherford (1871-1937) profoundly influenced modern
physics by formulating the first explanation of radioactivity. He
discovered two basic forms of radioactivity and in 1908 received
the Nobel Prize for chemistry for this work. He announced his
greatest discovery--the nuclear structure of the atom--in 1911.
Sir Ernest Rutherford (1871-1937) profoundly influenced modern
physics by formulating the first explanation of radioactivity. He
discovered two basic forms of radioactivity and in 1908 received
the Nobel Prize for chemistry for this work. He announced his
greatest discovery--the nuclear structure of the atom--in 1911.
 Erwin Schrodinger (1887-1961), an Austrian theoretical physicist,
published (1926) four papers that laid the
foundation of the wave-mechanics approach to quantum theory and
set forth his now-famous wave equation.
In 1933 he shared the
Nobel Prize for physics with Paul DIRAC for his contributions to
atomic theory.
He also worked on problems of general relativity and cosmology
and on a unified field theory. Late in his life Schrodinger
studied the foundations of physics and their implications for
philosophy.
Erwin Schrodinger (1887-1961), an Austrian theoretical physicist,
published (1926) four papers that laid the
foundation of the wave-mechanics approach to quantum theory and
set forth his now-famous wave equation.
In 1933 he shared the
Nobel Prize for physics with Paul DIRAC for his contributions to
atomic theory.
He also worked on problems of general relativity and cosmology
and on a unified field theory. Late in his life Schrodinger
studied the foundations of physics and their implications for
philosophy.
 Sir Joseph John Thomson (1856-1940), a pioneer in modern physics,
discovered the electron in 1895, revolutionizing existing theories
of atomic structure. Thomson is also recognized for his
investigations into the conduction of electricity through
gases--which earned him the 1906 Nobel Prize for physics--and for
his work on the mathematics of the electromagnetic-field theory
proposed by James Maxwell.
Sir Joseph John Thomson (1856-1940), a pioneer in modern physics,
discovered the electron in 1895, revolutionizing existing theories
of atomic structure. Thomson is also recognized for his
investigations into the conduction of electricity through
gases--which earned him the 1906 Nobel Prize for physics--and for
his work on the mathematics of the electromagnetic-field theory
proposed by James Maxwell.
 Hideki Yukawa (1907-1981), a Japanese physicist,
who won the Nobel Prize for physics in 1949, is known
for his theory of how the nuclear force holds the nucleus
together. As a result of this theory, he predicted (1935) the
existence of the meson, a subatomic particle, found in 1947 by
Cecil Powell.
Hideki Yukawa (1907-1981), a Japanese physicist,
who won the Nobel Prize for physics in 1949, is known
for his theory of how the nuclear force holds the nucleus
together. As a result of this theory, he predicted (1935) the
existence of the meson, a subatomic particle, found in 1947 by
Cecil Powell.
